If a website contains mixed content, it means that the site contains both secure (HTTPS) and insecure (HTTP) content. Mixed content usually occurs whenever SSL is installed and the website is migrated from HTTP to HTTPS. The site still contains all kinds of references to the ‘old’, HTTP address of the site.
Why is mixed content a problem?
Since the last decade, SSL encryption has become a must-have for all websites and web applications. If content such as images, scripts or other files are loaded over HTTP, the website visitor is vulnerable for ‘man-in-the-middle attacks’. This means that the insecure (non-encrypted) content could be read and altered by an attacker. This is especially dangerous when it concerns a webshop or other site processing payments or personal data, though SSL encryption is really a must for any website nowadays.
Browsers have also adopted SSL encryption as the default and will report websites without (correct) SSL implementation as not secure, or even block access to protect the visitor. Even when your site is loaded over SSL, your visitors might get ‘Not secure’ warnings when your site loads mixed content. Depending on the type of mixed content, some browsers will try to automatically fix the mixed content by loading the URL over HTTPS. In other cases, the content is not loaded at all. This would result in a site with missing images or broken functionality or styling.
How to detect mixed content?
It is highly recommended to check your site for mixed content after migrating the site from HTTP to HTTPS. Depending on the type of mixed content, browsers will indicate problems either via the ‘Not secure’ in the address bar, or via the browser console.
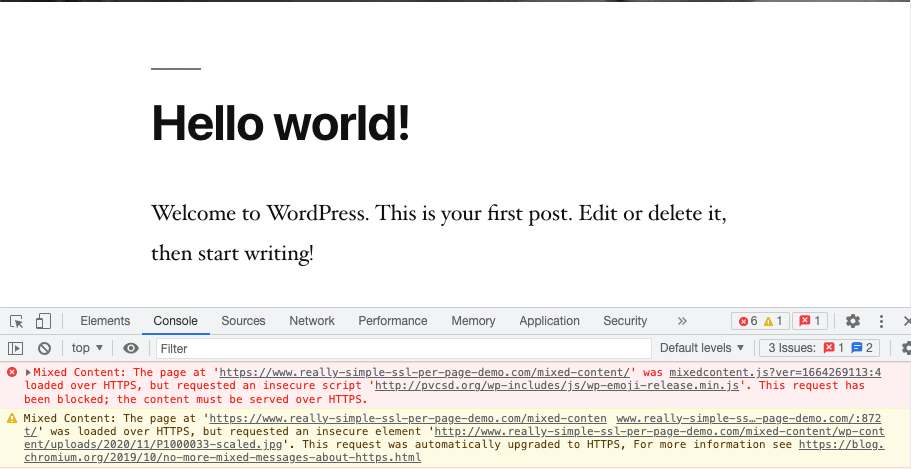
To access the browser console, right-click on the front end of the site, then inspect -> console. The screenshot below shows the browser console using Google Chrome. The first warning (in red) indicates that a JavaScript (.js) file is loaded over HTTP. As the browser is unable to fix the issue automatically, the request has been blocked. The second warning (in yellow) indicates that an image (.jpg) is loaded over HTTP. The browser managed to automatically resolve the issue by loading the image over HTTPS.
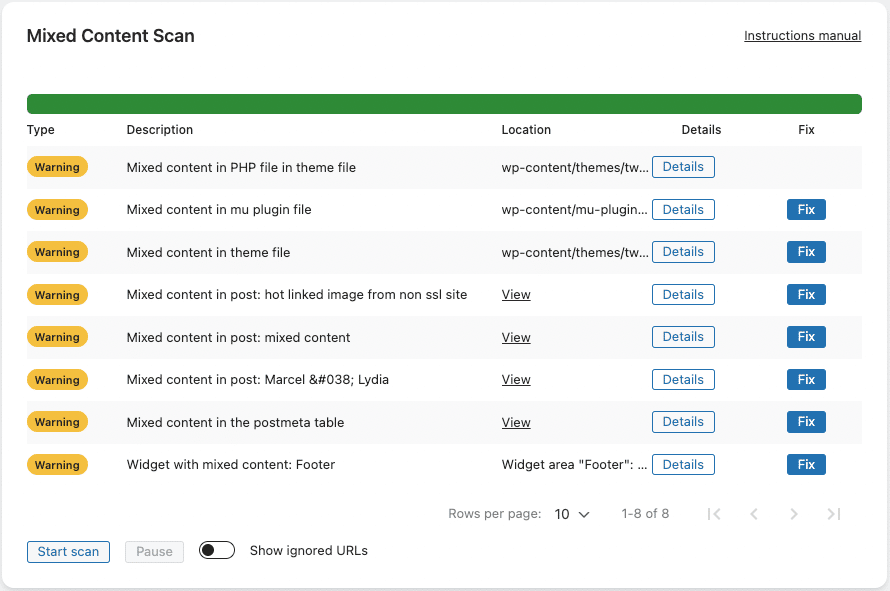
Really Simple SSL Pro contains an advanced mixed content scanner, which scans your entire WordPress website for all instances of Mixed content.
How to resolve mixed content?
To put it simple: whenever a site loads resources over HTTPS, there is no mixed content. For some websites the solution might really be as simple as a find and replace action for HTTP to HTTPS. Unfortunately, the solution is not as simple for most WordPress sites. A lot of themes or page builders dynamically generate CSS or JS files, which could still contain HTTP references.
The free Really Simple SSL plugin contains a mixed content fixer that will dynamically fix the most common mixed content issues. It does this without making any changes to the site’s database, so all changes will be reverted if you would decide to uninstall the plugin.
As mentioned, Really Simple SSL Pro contains an advanced mixed content scan to detect any remaining issues. The plugin will automatically fix 99% of all mixed content issues instantly. In some cases, your attention is required as Really Simple SSL Pro will need to make changes to the database, or download files to your server to be able to load them over HTTPS.